背景介绍
网络编程中,TCP/IP协议栈是基础中的基础。然而系统自带的网络协议栈通常封装太深,不便于理解内部机制。本文将通过约100行C语言代码,从零开始实现一个简化的TCP/IP协议栈,帮助你掌握以太网/IP/UDP/TCP的报文结构与处理流程。
虽然简化了很多细节,但该实现涵盖协议栈的关键模块,适合用于教学、原理验证或网络抓包分析器的内核构建。
协议结构简介
网络通信中常见的协议报文结构如下图所示:
- 以太网帧结构:
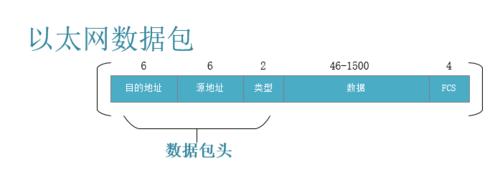
- IPv4头部结构:

- UDP头部结构:

- TCP头部结构:
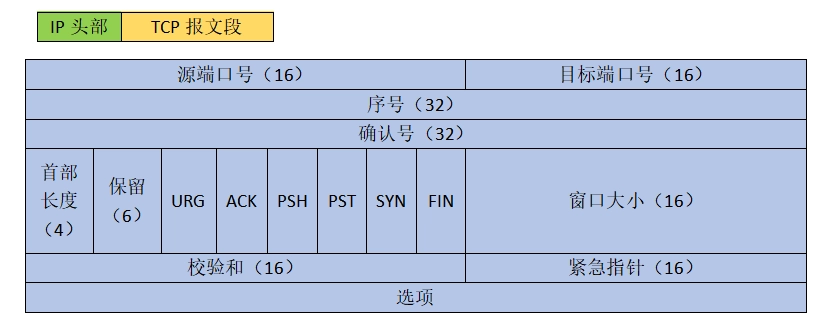
我们将以这些协议格式为基础,手动解析和构造数据包。
核心数据结构
我们从数据结构定义开始,模拟以太网、IP、UDP的头部布局:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| #define ETH_ADDR_LEN 6
struct ethhdr {
unsigned char dst_mac[ETH_ADDR_LEN];
unsigned char src_mac[ETH_ADDR_LEN];
unsigned short type;
};
struct iphdr {
unsigned char version:4, hdrlen:4;
unsigned char tos;
unsigned short totlen;
unsigned short id;
unsigned short flag:3, offset:13;
unsigned char ttl;
unsigned char proto;
unsigned short check;
unsigned int sip;
unsigned int dip;
};
struct udphdr {
unsigned short sport;
unsigned short dport;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short check;
};
struct udppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct udphdr udp;
unsigned char payload[0];
};
|
报文处理流程
主循环读取原始数据包
通过 poll 监听设备读取数据包(如通过 netmap 获取):
1
2
3
4
5
| if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) {
unsigned char *stream = NULL;
nty_nic_read(ctx, &stream);
nty_eth_process(ctx, stream);
}
|
分发以太网帧
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int nty_eth_process(nty_nic_context *ctx, unsigned char *stream) {
struct ethhdr *eh = (struct ethhdr*)stream;
if (ntohs(eh->type) == 0x0800) {
return nty_ipv4_process(ctx, stream);
} else if (ntohs(eh->type) == 0x0806) {
return nty_arp_process(ctx, stream);
}
return 0;
}
|
IP层解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int nty_ipv4_process(nty_nic_context *ctx, unsigned char *stream) {
struct iphdr *iph = (struct iphdr*)(stream + sizeof(struct ethhdr));
if (ip_fast_csum(iph, iph->hdrlen)) return -1;
if (iph->proto == 17) return nty_udp_process(ctx, stream);
else if (iph->proto == 6) return nty_tcp_process(ctx, stream);
else if (iph->proto == 1) return nty_icmp_process(ctx, stream);
return 0;
}
|
UDP处理和回应
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| int nty_udp_process(nty_nic_context *ctx, unsigned char *stream) {
struct udppkt *udp = (struct udppkt *)stream;
int udp_length = ntohs(udp->udp.len);
struct udppkt udp_rt;
nty_udp_pkt(udp, &udp_rt);
return nty_nic_write(ctx, &udp_rt, sizeof(struct udppkt));
}
void nty_udp_pkt(struct udppkt *udp, struct udppkt *udp_rt) {
memcpy(udp_rt, udp, sizeof(struct udppkt));
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.dst_mac, udp->eh.src_mac, ETH_ADDR_LEN);
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.src_mac, udp->eh.dst_mac, ETH_ADDR_LEN);
udp_rt->ip.sip = udp->ip.dip;
udp_rt->ip.dip = udp->ip.sip;
udp_rt->udp.sport = udp->udp.dport;
udp_rt->udp.dport = udp->udp.sport;
}
|
ping实现(ICMP协议)
使用原始套接字构造并发送ICMP Echo请求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
setsockopt(fd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &on, sizeof(on));
struct iphdr *ip_hdr = (struct iphdr *)packet;
struct icmphdr *icmp_hdr = (struct icmphdr *)(packet + sizeof(struct iphdr));
ip_hdr->version = 4;
ip_hdr->ihl = 5;
ip_hdr->tot_len = htons(sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + data_len);
ip_hdr->ttl = 64;
ip_hdr->protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP;
ip_hdr->saddr = 0;
ip_hdr->daddr = ip;
ip_hdr->check = 0;
icmp_hdr->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_hdr->checksum = Checksum((unsigned short *)icmp_hdr, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + data_len);
sendto(fd, packet, total_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&dst_addr, sizeof(dst_addr));
recvfrom(fd, packet, sizeof(packet), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&src_addr, &sock_len);
|
IP地址转换函数简介
| 函数 |
功能 |
inet_aton |
IP字符串 → 网络字节序数值 |
inet_addr |
IP字符串 → in_addr_t |
inet_ntoa |
in_addr → 点分十进制字符串 |
inet_pton |
表达 → 数值(支持IPv6) |
inet_ntop |
数值 → 表达(支持IPv6) |
示例:
1
2
3
4
| struct sockaddr_in addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET, "192.168.1.1", &addr.sin_addr);
char ip[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &addr.sin_addr, ip, sizeof(ip));
|
总结
通过约100行C语言代码,我们完成了一个简化但可运行的TCP/IP协议栈雏形,实现了:
- 以太网帧解析与协议识别
- IP头部分析与协议分发
- UDP回环通信
- ICMP Ping 报文生成与发送
这一项目是学习网络协议的绝佳实践方式。深入理解底层通信机制,对于网络编程、安全分析、驱动开发等领域大有裨益。
延伸阅读
如你希望在此基础上继续支持TCP连接状态管理、三次握手、重传机制等,可逐步构建完整的协议栈模拟器。



