如果中序遍历为有序的话则为二叉搜索树,为了避免退化为单链表,加入平衡规则后保持平衡则为平衡二叉树,搜索的时间复杂度为O(lgn).
满二叉树、完全二叉树又推出最大堆、最小堆(堆排序、定时器)。平衡二叉树又推出avl、红黑树。
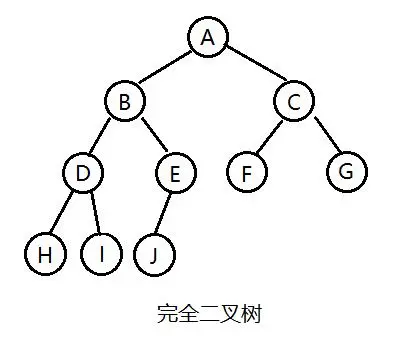
对于深度为K的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时称之为完全二叉树。
二叉树的递归遍历
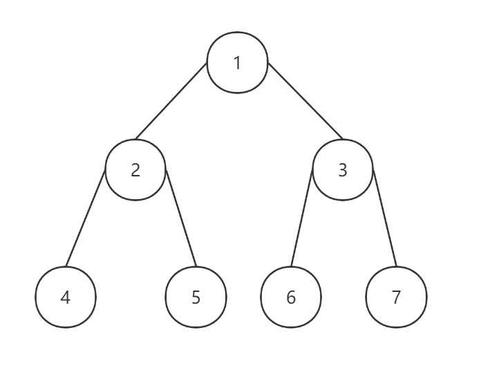
前序遍历:根->左->右,1>2>4>5>3>6>7,245这棵树是作为一个整体子树从根节点遍历,这就是递归的思想。
中序遍历:左->根->右,4>2>5>1>6>3>7,每次遍历到子树也是重新左->根->右进行遍历。
后序遍历:左->右->根,4>5>2>6>7>3>1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| void PreOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
result.push_back(root->val);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
InOrder(root->left);
result.push_back(root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
result.push_back(root->val);
}
|
二叉树的迭代遍历
栈是先进后出,前序遍历:根->左->右,1>2>4>5>3>6>7,所以要从右边往左进行压栈,顺序为右->左->根,思维方式恰好相反。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| void PreOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (node != nullptr) {
if (node->right != nullptr) st.push(node->right);
if (node->left != nullptr) st.push(node->left);
st.push(node);
st.push(nullptr);
} else {
node = st.top(); st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
}
void InOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (node != nullptr) {
if (node->right != nullptr) st.push(node->right);
st.push(node);
st.push(nullptr);
if (node->left != nullptr) st.push(node->left);
} else {
node = st.top(); st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
}
void PostOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (node != nullptr) {
st.push(node);
st.push(nullptr);
if (node->right != nullptr) st.push(node->right);
if (node->left != nullptr) st.push(node->left);
} else {
node = st.top(); st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
}
|
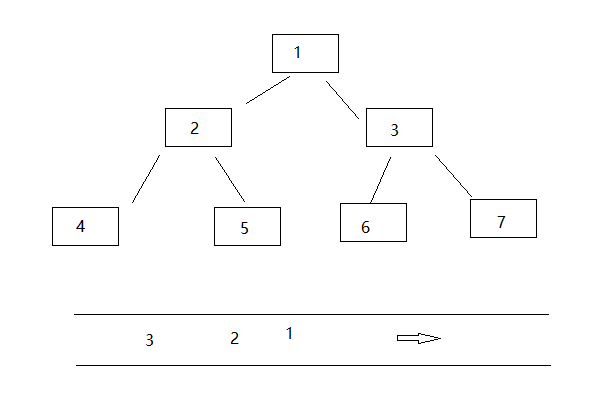
二叉树的层序遍历
广度优先搜索,需要使用队列来实现,和迭代类似,也是要让根节点先入,根节点弹出队列前,要把左右子节点入队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| vector<int> traverse(TreeNode *root)
{
vector<int> result;
if (root == nullptr) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
size_t size = que.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode *node = que.front(); que.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> traverse(TreeNode *root)
{
vector<vector<int>> result;
if (root == nullptr) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
size_t size = que.size();
vector<int> res;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode *node = que.front(); que.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(res);
}
}
|
二叉树树形dp
求最优解问题、且子问题的解有重叠(某个节点的解是其父节点的一部分),需要找到状态转移方程。
从二叉树的节点A出发,可以向上或向下走,但沿途的节点只能经过一次,当达到节点B时,路径上的节点树叫做A到B到距离。
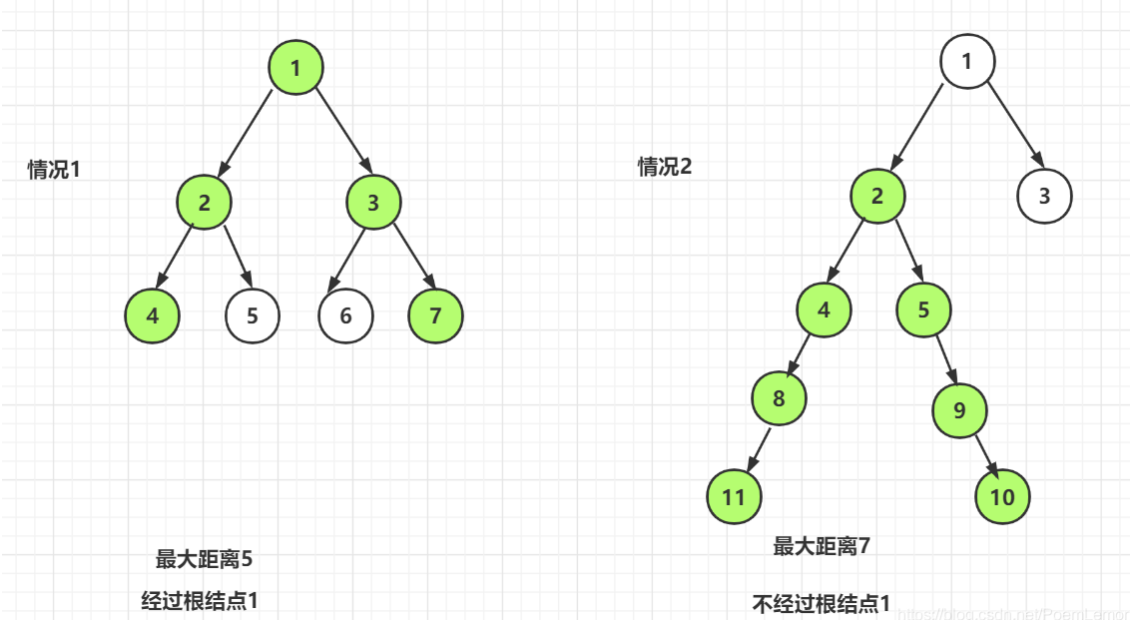
这棵树的最大距离(首先构建出这个模型,和高中的受力分析意义画出图来):max(左子树的最大距离,右子树的最大距离,左子树的高度+右子树的高度+1)
子问题的解有重叠:f(n-1)是f(n)解的一部分,确定边界值为某个叶子节点的解为f(0)=max(0, 0, 1)=1。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| struct RetVal {
int distance;
int height;
RetVal(int dis, int hgt) : distance(dis), height(hgt) {}
};
int Do(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
return dfs(root).distance;
}
RetVal dfs(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return RetVal(0, 0);
RetVal left = dfs(root->left);
RetVal right = dfs(root->right);
int height = std::max(left.height, right.height) + 1;
return RetVal(std::max(std::max(left.distance, right.distance), left.height + right.height + 1), height);
}
|
翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。

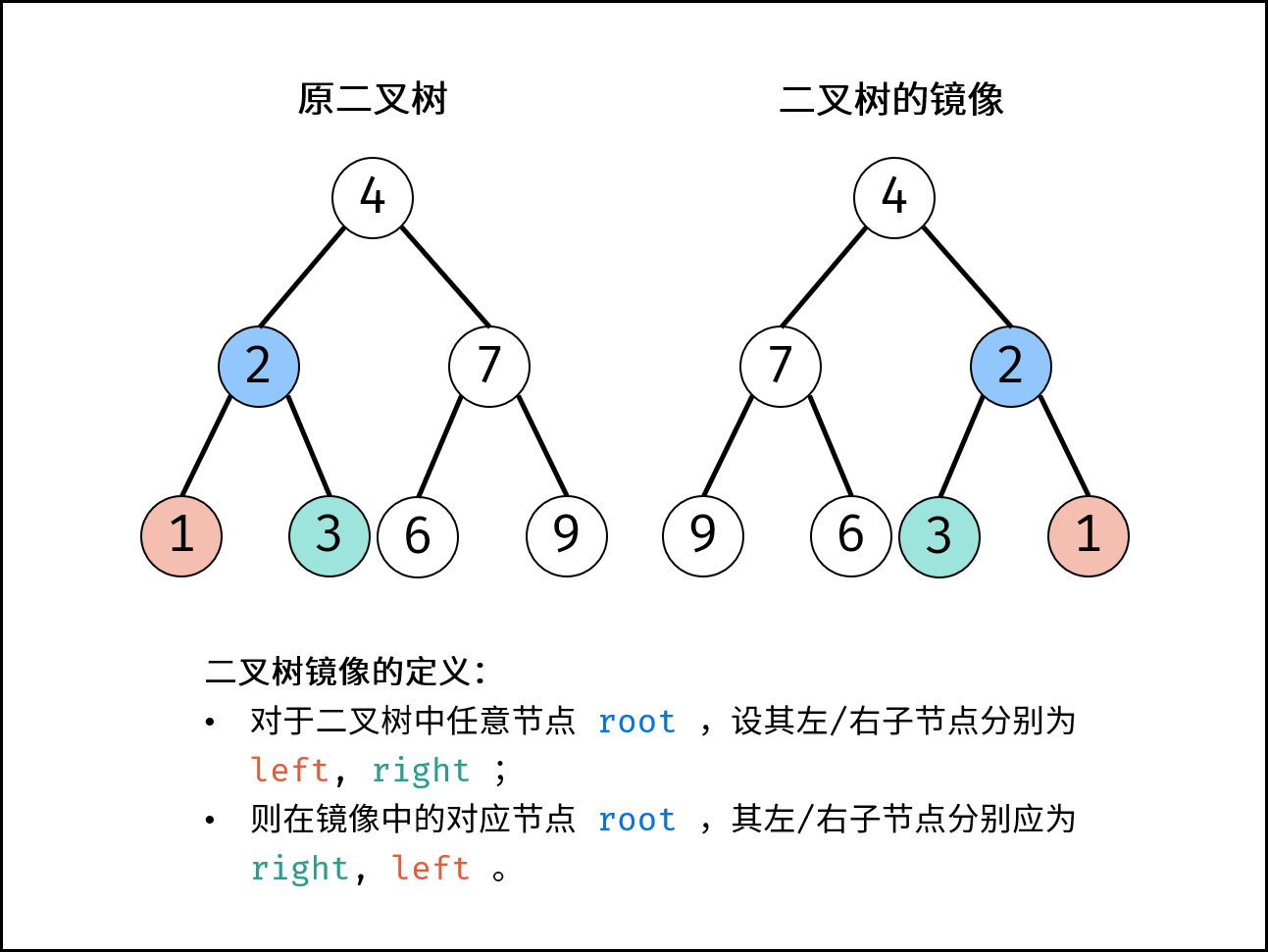
根据二叉树镜像的定义,考虑递归遍历(dfs)二叉树,交换每个节点的左 / 右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像。
Q: 为何需要暂存 root 的左子节点?
A: 在递归右子节点 “root.left=invertTree(root.right);” 执行完毕后, root.left 的值已经发生改变,此时递归左子节点 invertTree(root.left) 则会出问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
root->left = invertTree(root->right);
root->right = invertTree(tmp);
return root;
}
|
利用栈(或队列)遍历树的所有节点 nodenodenode ,并交换每个 nodenodenode 的左 / 右子节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (node->left != nullptr) stack.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) stack.push(node->right);
TreeNode* tmp = node->left;
node->left = node->right;
node->right = tmp;
}
return root;
}
|
二叉搜索树中的插入操作
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果。
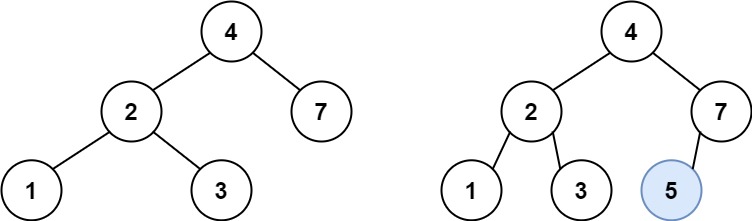
根据二叉搜索树的性质,可以巧妙的将待插入结点转变为叶子结点插入,从而避免改变二叉树原有整体结构。 原因:二叉树搜索树本身就是有序的,按照其有序性,遍历找到目标val位置,一定能找到空子树,即NULL,此时构建新节点,将val插入即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root == NULL) return new TreeNode(val);
if(root->val > val) root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
else root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
return root;
}
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root == NULL) return new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->val > val){
if (cur->left == NULL){
cur->left = new TreeNode(val);
break;
} else {
cur = cur->left;
}
} else {
if (cur->right == NULL) {
cur->right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
} else {
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
return root;
}
|
二叉树最大深度?
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
思路:
使用两个栈,一个用于存储节点,另一个用于存储节点的深度。我们从根节点开始,逐层遍历树的节点,同时记录每个节点的深度。最终,返回最大深度作为结果。这种方法避免了递归,减小了函数调用栈的开销。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
std::stack<TreeNode*> nodes;
std::stack<int> depths;
int max = 0;
nodes.push(root);
depths.push(1);
while (!nodes.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
int depth = depths.top();
depths.pop();
max = std::max(max, depth);
if (node->left) {
nodes.push(node->left);
depths.push(depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) {
nodes.push(node->right);
depths.push(depth + 1);
}
}
return max;
}
|






